Creating a green and sustainable garden is more achievable than you might think! This article explores 10 innovative ideas to transform your outdoor space into an environmentally friendly haven. Learn how to implement eco-friendly gardening practices, from choosing the right plants to utilizing sustainable gardening materials and techniques. Discover practical tips for water conservation, pest control, and soil enrichment that will benefit both your garden and the planet. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, these ideas will help you cultivate a beautiful and environmentally responsible garden.
Rainwater Harvesting Systems
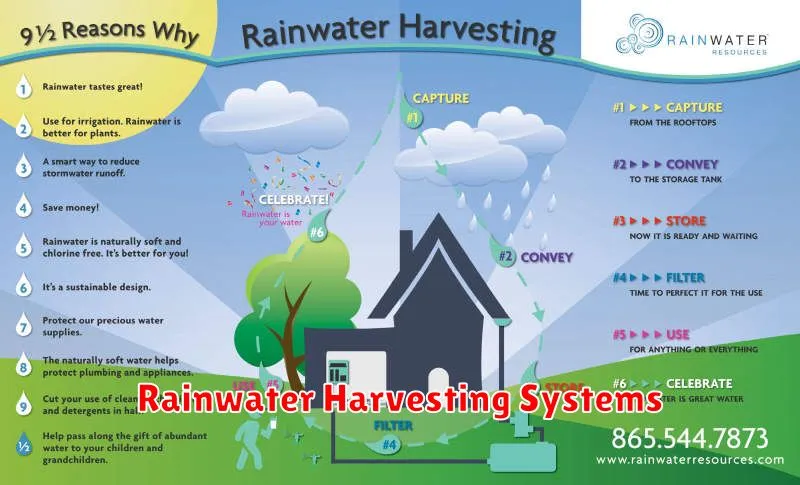
Rainwater harvesting systems are designed to collect and store rainwater for later use. This sustainable practice offers numerous benefits, including reducing reliance on municipal water supplies, conserving water resources, and mitigating the impact of droughts.
These systems typically involve several key components. A roof catchment area collects rainwater, channeling it through a gutter system and into a storage tank. Filtration is crucial to remove debris and impurities, often employing techniques like screening and sedimentation. A first-flush diverter helps eliminate the initial, heavily contaminated rainwater runoff.
The size and type of storage tank vary depending on the system’s scale and intended use. Materials commonly used include concrete, plastic, and steel. The water quality within the tank needs to be regularly monitored and treated as necessary to prevent contamination and ensure its suitability for the intended purpose.
Applications for harvested rainwater are diverse. It can be used for non-potable purposes such as irrigation, toilet flushing, and vehicle washing. With proper treatment, it can also be used for potable purposes, though this requires more stringent filtration and disinfection procedures.
The design and installation of a rainwater harvesting system require careful consideration of several factors, including the size of the catchment area, the average rainfall, the desired storage capacity, and the intended use of the harvested water. Professional consultation is often recommended to ensure optimal performance and compliance with relevant regulations.
The economic viability of rainwater harvesting systems can be influenced by factors such as initial installation costs, long-term maintenance expenses, and potential water savings. In many cases, the long-term benefits in terms of water conservation and reduced water bills significantly outweigh the initial investment.
Compost Bins for Organic Waste

Compost bins are essential tools for anyone looking to manage organic waste effectively and sustainably. They provide a contained environment for the decomposition of organic materials, such as food scraps, yard waste, and other biodegradable materials, transforming them into valuable compost. This process not only reduces landfill waste but also creates a nutrient-rich soil amendment beneficial for gardens and landscaping.
Various types of compost bins cater to different needs and preferences. Rotating compost bins, for instance, allow for easy turning of the compost pile, accelerating the decomposition process. Static compost bins, often constructed from wood or plastic, offer a simpler, more stationary option. The choice depends on factors such as available space, the volume of waste generated, and personal composting methods.
Proper construction and management of a compost bin are crucial for successful composting. Adequate ventilation is essential to maintain aerobic conditions, preventing foul odors and promoting efficient decomposition. Maintaining a proper balance of “greens” (nitrogen-rich materials like food scraps) and “browns” (carbon-rich materials like dried leaves) is also vital for optimal composting. Regular turning of the compost, especially in static bins, helps to aerate the material and speed up the breakdown process.
Benefits of using compost bins extend beyond waste reduction. The resulting compost enriches soil, improving its structure, water retention, and nutrient content. This reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, contributing to a healthier and more environmentally friendly gardening practice. Furthermore, composting significantly reduces the amount of organic waste sent to landfills, lessening methane emissions and promoting a circular economy.
In conclusion, investing in a compost bin is a worthwhile endeavor for individuals and communities committed to sustainable waste management. By choosing the right bin and employing appropriate composting techniques, you can effectively manage organic waste, create valuable compost, and contribute to a healthier environment. The environmental and horticultural advantages are significant and long-lasting.
Native Plant Selection
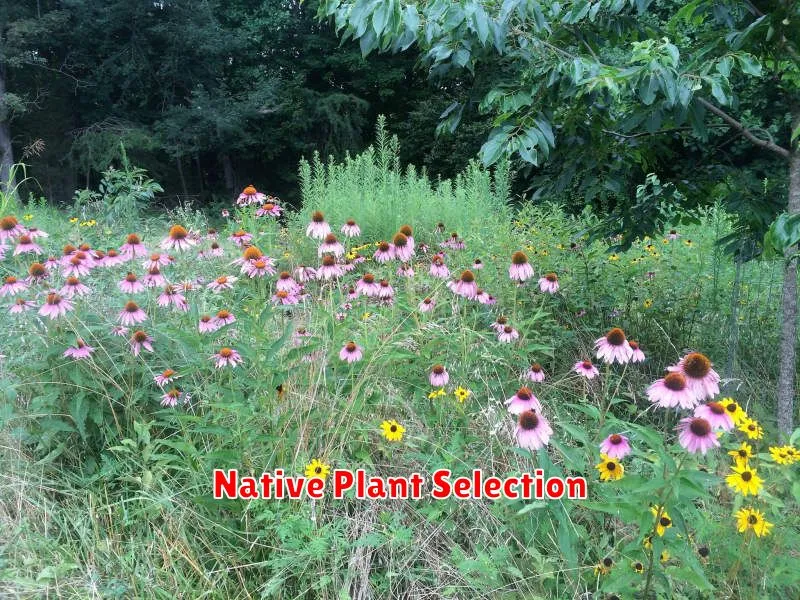

Selecting native plants for your landscape offers numerous benefits beyond aesthetic appeal. These plants are naturally adapted to the local climate and soil conditions, requiring less water, fertilizer, and pesticides compared to non-native species. This translates to reduced environmental impact and lower maintenance costs for the homeowner.
Biodiversity is significantly enhanced through the use of native plants. They provide crucial habitat and food sources for local wildlife, including birds, insects, and pollinators. This contributes to a healthier and more resilient ecosystem in your immediate surroundings.
When choosing native plants, consider the specific characteristics of your site. Factors such as sunlight exposure, soil type, and moisture levels will influence which species will thrive. Consulting with local nurseries or horticultural experts can provide valuable guidance in selecting appropriate plants for your individual needs.
The long-term benefits of native plant selection are substantial. These plants are generally more resistant to pests and diseases, requiring less intervention from the gardener. Their established root systems contribute to soil stabilization and erosion control, further enhancing the ecological value of your property.
Ultimately, incorporating native plants into your landscape is a responsible and rewarding endeavor. It fosters a healthier environment, reduces maintenance demands, and contributes to the overall beauty and biodiversity of your surroundings. The investment in native species yields significant returns in ecological benefits and aesthetic satisfaction.
Solar-Powered Garden Lights

Solar-powered garden lights offer a convenient and environmentally friendly way to illuminate outdoor spaces. These lights harness the power of the sun during the day, storing energy in rechargeable batteries to provide illumination at night. This eliminates the need for electrical wiring, making installation simple and reducing reliance on the power grid.
One of the key advantages of solar garden lights is their sustainability. They reduce carbon emissions associated with traditional electricity consumption, contributing to a smaller environmental footprint. Furthermore, they are typically low-maintenance, requiring minimal upkeep beyond occasional cleaning of the solar panels.
However, the effectiveness of solar garden lights is dependent on sunlight exposure. The amount of light produced can vary based on weather conditions and the duration of daylight hours. In areas with limited sunlight, the lights may not perform as optimally.
Different types of solar garden lights are available to suit various needs and aesthetics. These include stake lights, path lights, and hanging lanterns, each offering unique design features and levels of brightness. Choosing the appropriate style will depend on the specific requirements of the garden or outdoor area.
When selecting solar garden lights, it’s essential to consider factors such as the brightness (measured in lumens), battery life, and the overall durability of the product. Reading customer reviews and comparing specifications from different brands can help in making an informed decision.
In conclusion, solar-powered garden lights provide an attractive and sustainable solution for outdoor lighting. While their effectiveness depends on sunlight availability, their ease of installation, low maintenance, and environmental benefits make them a popular choice for homeowners and gardeners alike.
Bee and Butterfly Gardens

Creating a bee and butterfly garden is a rewarding way to support these vital pollinators and add beauty to your landscape. These insects are essential for a healthy ecosystem, and providing them with a suitable habitat is crucial for their survival.
The key to success lies in selecting the right plants. Both bees and butterflies have specific preferences. Butterflies are attracted to brightly colored flowers with flat or shallow blossoms, making it easier for them to access nectar. Consider planting varieties like milkweed, coneflowers, zinnias, and butterfly bush.
Bees, on the other hand, appreciate a diverse range of flowers with varying shapes and sizes. They are particularly drawn to flowers rich in pollen and nectar. Include plants like lavender, sunflowers, salvia, and bee balm in your garden design. Planting a variety of flowering plants that bloom at different times throughout the growing season ensures a continuous food source for your pollinators.
Location also plays a significant role. Choose a sunny spot that receives at least six hours of sunlight per day. Provide a water source, such as a shallow dish of water with pebbles, to help keep the insects hydrated. Avoid using pesticides, as these chemicals can harm both bees and butterflies.
Beyond the plants, consider adding other features to enhance your garden’s appeal to pollinators. A habitat-friendly environment might include leaving some areas unmowed to provide nesting sites, and adding rocks or logs to create shelter. With a little planning and effort, you can create a vibrant and thriving bee and butterfly garden that will benefit both you and the environment.
DIY Vertical Herb Garden

Creating a vertical herb garden is a fantastic way to maximize space and add a touch of green to your home or patio. This project is surprisingly easy and requires minimal materials, making it perfect for beginner gardeners.
Materials you will need: A wooden pallet (ensure it’s treated for outdoor use if placing it outside), potting soil, your choice of herb seedlings or seeds, a drill with a large drill bit (for drainage), and optional: decorative elements such as paint or stain.
Step-by-step instructions: First, clean your wooden pallet thoroughly. Next, use your drill to create drainage holes in the bottom of each section where you plan to plant. This prevents waterlogging and helps your herbs thrive. Fill each section with potting soil, leaving a little space at the top. Then, gently plant your herb seedlings or seeds, following the instructions on the packaging. Finally, water your new garden and find a sunny spot to place it.
Optional enhancements: To personalize your vertical garden, consider staining or painting the pallet. You can also add small labels to each section to easily identify your herbs. Using different varieties of herbs adds visual interest and allows you to easily harvest what you need for cooking.
Maintenance: Regular watering is crucial. Check the soil moisture regularly and water when it feels dry. Fertilizing your herbs every few weeks will help promote healthy growth. You may need to trim your herbs periodically to prevent overcrowding and encourage bushier growth.
With a little effort, you can enjoy a beautiful and productive vertical herb garden. This DIY project provides fresh herbs right at your fingertips, enhancing your culinary creations and adding a touch of nature to your living space.
Eco-Friendly Paving Solutions

Traditional paving materials often have significant environmental drawbacks. Asphalt, for instance, relies heavily on petroleum, a finite resource, and its production contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Concrete, while durable, requires substantial energy consumption during manufacturing and contributes to carbon footprint.
Fortunately, a growing number of eco-friendly paving alternatives are emerging, offering sustainable and environmentally responsible solutions. These options aim to reduce the environmental impact throughout the material’s lifecycle, from production to disposal.
Permeable paving is one such solution. Materials like porous concrete and permeable interlocking pavers allow rainwater to seep through, reducing runoff and replenishing groundwater supplies. This helps to mitigate flooding and improve water quality. They also reduce the urban heat island effect.
Recycled materials are another key component of sustainable paving. Recycled plastic, rubber from recycled tires, and even glass can be incorporated into paving mixes, diverting waste from landfills and reducing reliance on virgin materials. This contributes to a circular economy.
Plant-based materials, such as stabilized soil and bio-binders, are also gaining traction. These options offer a lower carbon footprint compared to traditional materials, and can integrate seamlessly with natural landscapes.
The selection of an eco-friendly paving solution should consider several factors including project requirements, budget, and local environmental conditions. However, the long-term benefits of reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability make these alternatives a compelling choice for environmentally conscious projects.
Drip Irrigation Systems

Drip irrigation, also known as trickle irrigation, is a type of micro-irrigation system that saves water and fertilizer by delivering water directly to the roots of plants. This method is highly efficient, minimizing water waste compared to traditional flood or sprinkler systems.
Key Advantages of drip irrigation include: Water conservation through precise delivery, reduced weed growth due to targeted watering, improved fertilizer use efficiency minimizing runoff, and enhanced plant growth resulting in higher yields.
System Components typically consist of a water source, a filter to remove debris, a pressure regulator to maintain consistent flow, a network of tubing and emitters delivering water to individual plants, and potentially a fertilizer injector for nutrient delivery.
Types of Emitters vary, including in-line emitters integrated into the tubing, and separate drippers which can be adjustable for flow rates. Choosing the right emitter depends on factors such as plant type and soil conditions.
Installation can range from simple DIY projects for small gardens to complex systems requiring professional installation for large-scale agricultural applications. Proper planning and design are crucial for effective operation.
Maintenance is relatively low, primarily involving checking for leaks, clogged emitters, and ensuring proper pressure. Regular cleaning helps prevent blockages and prolong system lifespan.
While the initial cost can be higher compared to other irrigation methods, the long-term cost savings from water and fertilizer conservation, coupled with the improved crop yields, make drip irrigation a worthwhile investment.
Recycled Garden Decor

Transforming discarded items into beautiful and functional garden decorations is a rewarding and environmentally friendly endeavor. With a little creativity and some elbow grease, you can create unique pieces that add character and charm to your outdoor space. The possibilities are truly endless!
Recycled materials offer a plethora of options. Old tires can be upcycled into vibrant planters, adding a pop of color and texture. Broken pottery and tiles can be used to create stunning mosaics for pathways or walls. Glass bottles can be repurposed into whimsical hanging planters or quirky garden stakes.
Metal objects, such as old cans and tins, can be painted and used as unique planters or decorative elements. Wooden pallets can be disassembled and used to build raised garden beds or charming fences. Even plastic containers can find a new life as seedling starters or protective covers for delicate plants.
The key to successful recycled garden decor is to embrace your imagination. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different materials and techniques. A simple coat of paint can transform an ordinary object into something extraordinary. Adding embellishments like buttons, beads, or shells can also add a personalized touch.
Creating recycled garden decor not only adds beauty to your garden but also promotes sustainability. By giving new life to discarded items, you’re reducing waste and minimizing your environmental impact. It’s a fun, fulfilling activity that allows you to express your creativity while contributing to a greener planet.
Wildlife Habitat Zones

Wildlife habitat zones are areas that provide the necessary resources for animals to survive and thrive. These resources include food, water, shelter, and space. The specific needs vary greatly depending on the species of animal, but all animals require these basic necessities.
Different habitats support different types of wildlife. For instance, a forest habitat will provide shelter and food sources suitable for forest-dwelling animals like deer, owls, and squirrels. Conversely, a grassland habitat supports creatures adapted to open spaces, such as bison, prairie dogs, and certain bird species.
The quality of a habitat zone is crucial for the health of its inhabitants. Factors like habitat fragmentation (breaking up large habitats into smaller, isolated patches), pollution, and climate change can significantly degrade the quality of a habitat, negatively affecting wildlife populations.
Conservation efforts often focus on protecting and restoring wildlife habitat zones. This might involve creating protected areas like national parks, restoring degraded habitats, or establishing wildlife corridors to connect isolated populations.
Understanding the different types of habitat zones and the specific needs of the animals within them is vital for effective wildlife management and conservation. This knowledge allows for the development of targeted strategies to protect biodiversity and ensure the long-term survival of wildlife populations.

